The International Motor Insurance System is a protection mechanism for victims of cross-border traffic accidents
The Green Card System is the International Motor Insurance System created in 1949, following a recommendation of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) based on Recommendation no. 5 adopted by the Working Group on Road Transport of the Inland Transport Committee. This international agreement facilitates vehicle movement between member countries. The Principality of Andorra joined in 1996.
The objectives of the 'Green Card System' are:
- Border crossing: to facilitate international travel by exempting drivers from member countries visiting other member countries from having to purchase an insurance policy every time they cross a border, provided they are insured in their own country.
- Claim settlement: to ensure that victims of cross-border traffic accidents, caused by a driver from a member country, are duly compensated in accordance with the rules governing compulsory civil liability insurance for vehicles accidents in the country where the accident occurred. The goal is that victims are not disadvantaged because the accident was caused by a foreign vehicle.
- Purpose of the system: To enable a vehicle from country A to travel through country B while being covered by the original car insurance policy from country A.
Its members are:
- The Green Card System consists of 46 National Bureaux, representing approximately 1,500 motor insurance companies across 50 countries in Europe, North Africa and the Middle East. These are recognized by their national authorities and ensure the system functions effectively.
- A National Insurance Bureau or Green Card Bureau is an organization established in each country that is a member of the International Motor Insurance System or Green Card System. It guarantees that a victim suffering damage from a traffic accident caused by a foreign vehicle (originating from another country within the system) will be compensated in the country where the accident happened. The National Insurance Bureau of the country of the accident may subsequently recover all compensations from the Bureau of the country from which the responsible vehicle originates. Therefore, the National Bureau handles claims and settles accidents involving foreign vehicles. The different National Bureaux collaborate on the basis of a Bilateral Internal Agreement signed between each of them.
- All members belong to an international non-governmental organization called the Council of Bureaux (COB), which has its secretariat in Brussels.
- The Council of Bureaux (COB) is responsible for protecting victims of cross-border traffic accidents.
- The different National Insurance Bureaux are governed by the General Regulations of the Council of Bureaux (COB) and are recognized and approved by their respective governments. Each Bureau represents the motor civil liability insurance companies of its country.
The National Bureaux of each country in the International Motor Insurance System follow common operational standards.
What are the roles of the members?
The two main functions of each Bureau are to manage and resolve claims arising from accidents:
- Caused in their territory by vehicles registered in other countries. In such cases, the Bureau acts as 'Accident Country Bureau' or 'Handling Bureau' and is responsible for managing and settling claims, in accordance with the national legal provisions on compulsory civil liability insurance for vehicle accidents, the management and settlement of claims from accidents caused by visiting vehicles.
- Caused in other countries by vehicles registered in their territory. In these cases, the Bureau acts as the 'Guaranteeing Bureau' and guarantees the Motor Insurance Certificates or Green Cards issued by the insurance companies associated with their policyholders.
The bureaux also supervise the issuance of international insurance certificates, better known as Green Cards, by insurance entities that belong to the National Bureau in each country.
Geographical scope
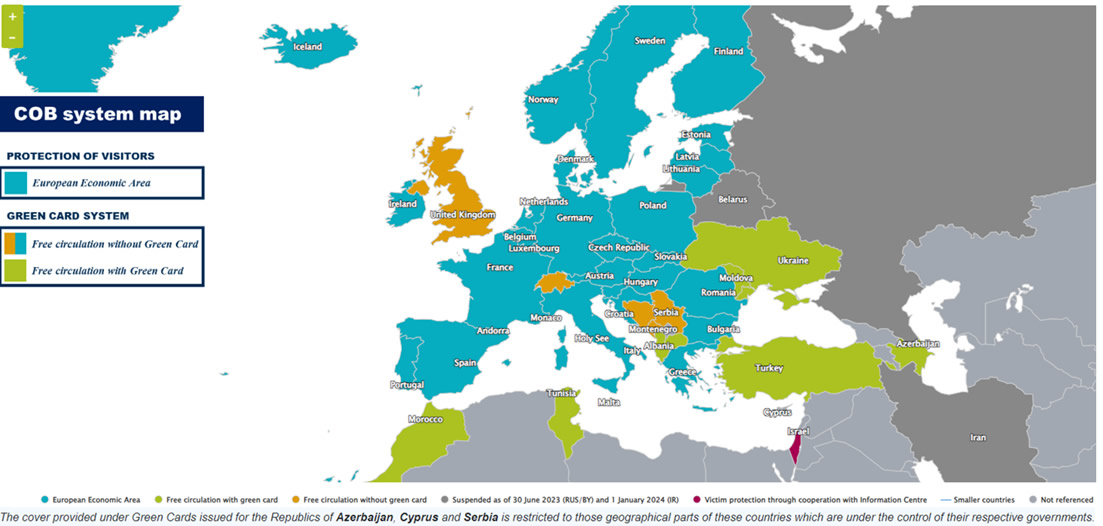
The Green Card System is primarily, but not exclusively, a European system.
The geographical scope of the Green Card System extends to:
- European countries located West of the Ural Mountains and the Caspian Sea
- Countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea
In addition to the existing members of the Green Card System, the following countries are eligible for future COB membership: Algeria, Armenia, Egypt, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Lebanon, Libya and Syria.
The following countries are currently suspended from the Green Card System: Russia, Belarus and Iran.
Inter-Bureaux Relations:
The different National Bureaux collaborate based on Internal Regulations signed bilaterally between them.
The introduction of the Green Card System was an important step in facilitating international traffic. However, presenting a document at each border still takes time and creates obstacles to the free movement of people and goods.
According to a 1972 Motor Vehicle Directive, EU member states form a single territory where insurance is mandatory, but Green Card checks at borders have been abolished.
Encouraged by European initiatives, several member countries of the Green Card System replaced the Green Card or International Insurance Certificate with a Multilateral Agreement, the Multilateral Agreement - MA (Section III of the General Regulations of the Green Card System), where the vehicle registration serves as proof of insurance instead of the Green Card.
Today, this international agreement covers the following 36 countries:
- The 27 Member States of the European Union;
- 3 additional countries participating in the European Economic area: Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway
- 6 additional countries participating in this system by way of agreement: Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Serbia, Switzerland and the United Kingdom.
The MA Signatory Bureaux recognise each other's Motor Third Party Liability Insurance (MTPL) based on the origin of the vehicle (based on the notion of `territory in which a vehicle is normally based', as described in article 1.4 of the EU Codified Directive EU MID IV). In most cases, a motor vehicle is typically located in the territory of the country where it is registered.
As a result, in the countries of the multilateral agreement, the Green Card is no longer a mandatory document required for crossing borders by drivers.
The National Bureau of the country where the vehicle is usually located guarantees the reimbursement of all damages caused by this vehicle in other countries, even if the vehicle is not properly insured.
The National Bureaux of each country adhering to the International Motor Insurance System follow common operational standards.
These countries are listed on the back of your Green Card and can also be found on the Green Card System country list or the Council of Bureaux website.
However, the formality of presenting the Green Card remains in effect for the remaining eleven countries of the Green Card System (Section II of the General Regulations of the Green Card System). In these countries, insurance is also mandatory, and Green Card border checks have been maintained.
Non-signatory countries to the Multilateral Agreement where the Green Card is required:
![]() AL - Albània Joined in 1992
AL - Albània Joined in 1992
![]() AZ - Azerbaitjan Joined in 2016
AZ - Azerbaitjan Joined in 2016
![]() BY - Bielorússia (suspended as of 30/06/2023)
BY - Bielorússia (suspended as of 30/06/2023)
![]() IR - Iran (suspended as of 10/01/2026)
IR - Iran (suspended as of 10/01/2026)
![]() MA - Marroc Joined in 1969
MA - Marroc Joined in 1969
![]() MD - Moldàvia Joined in 1997
MD - Moldàvia Joined in 1997
![]() RUS - Rússia (suspended as of 30/06/2023)
RUS - Rússia (suspended as of 30/06/2023)
![]() TN - Tunísia Joined in 1969
TN - Tunísia Joined in 1969
![]() TR - Turquia Joined in 1964
TR - Turquia Joined in 1964
![]() UA - Ucraïna Joined in 1997
UA - Ucraïna Joined in 1997
You can also find them on the Council of Bureaux website.
You can also access the contacts of the National Bureaux network of the Green Card System on the Council of Bureaux website.